Many businesses struggle with aging ERP systems that no longer meet their evolving needs, resulting in inefficiencies, data inaccuracies, and employee frustration. When faced with this challenge, organizations must decide whether to upgrade their existing ERP system or re-implement it from scratch.
This guide explains when each option is most appropriate and highlights the specific benefits and challenges businesses may encounter with each approach. By the end of this article, you'll be well-equipped to make an informed decision for your ERP strategy. Let’s start the journey!
Understanding ERP Upgrade
An ERP upgrade involves updating the existing ERP system to a newer version. This process keeps the core system intact while enhancing it with the latest features and improvements. It is similar to renovating a house rather than building a new one from the ground up.
When to Choose Upgrade:
In certain situations, upgrading your existing ERP system may be a more suitable option than re-implementation. A recent survey revealed that 43% of companies are interested in upgrading their ERP systems.
Here are the key circumstances in which an upgrade is the best choice:

1. Incremental Improvements
Upgrades are suitable when the goal is to benefit from newer features and improvements without overhauling the entire system. This approach allows organizations to incrementally enhance their ERP capabilities without disrupting their operations.
2. Compatibility and Support
Upgrades are necessary to maintain vendor support and compatibility with other integrated systems. ERP vendors typically provide support for only the latest versions of their software. Upgrading ensures that the organization remains within the supported version range and can access technical assistance and updates.
3. Budget Constraints
When the organization has budget constraints and cannot afford a full re-implementation, upgrading the existing system is a cost-effective alternative. It allows the organization to take advantage of new features without incurring the higher costs associated with re-implementation.
Benefits of Upgrade:
An ERP upgrade from the right partner can enhance existing systems without the need for a total re-implementation. Following are the key advantages of upgrading your ERP system:
1. Cost-Effective
Upgrading is typically less expensive than re-implementation. It involves lower costs for software licenses, implementation, and training. Organizations can achieve significant improvements in functionality and performance without the financial burden of starting from scratch.
2. Less Disruptive
Upgrading is generally less disruptive to business operations compared to re-implementation. Since the core system remains the same, users can continue to work with familiar processes and interfaces, minimizing downtime and ensuring continuity.
3. Familiarity
Users are already familiar with the system, reducing the need for extensive retraining. This can accelerate the adoption of new features and minimize resistance to change within the organization.
Challenges of Upgrade:
When upgrading ERP systems, organizations may face the following challenges:
1. Technical Debt
Upgrading can carry forward legacy issues and technical debt. If the existing system has accumulated inefficiencies or problematic customizations over time, these issues may persist even after the upgrade.
2. Complexity
Depending on the extent of customizations and integrations, upgrades can be complex and require significant technical expertise. Ensuring that all customizations and integrations work seamlessly with the new version can be challenging.
3. Limited Process Changes
Upgrading offers less opportunity for rethinking and optimizing business processes compared to re-implementation. Organizations may find it challenging to achieve the same level of process improvement without a complete overhaul.
Understanding ERP Re-implementation
ERP re-implementation involves starting afresh with a completely new installation of the ERP system. This process usually entails deploying the latest version of the ERP software as if it were a new implementation. It is akin to moving into a brand-new house rather than renovating an old one.
When to Choose Re-implementation:
Deciding between ERP re-implementation and upgradation can be a critical choice for organizations. Here are some of the scenarios in which re-implementation is the most appropriate option:
1. Significant Process Changes
Re-implementation is ideal when there are substantial changes in business processes that the current ERP system cannot accommodate efficiently. For example, if a company has undergone a major merger or acquisition, its processes and workflows might have changed significantly, necessitating a complete overhaul of the ERP system.
2. Outdated Customizations
Many organizations customize their ERP systems to meet specific needs. Over time, these customizations can become outdated or incompatible with newer versions of the software. Re-implementing allows the organization to shed these legacy customizations and build a system that leverages current best practices and technologies.
3. Technological Leap
If the existing ERP system is significantly outdated, a re-implementation can help the organization take advantage of new technological advancements. This is especially relevant when moving from on-premises solutions to cloud-based ERP systems, which offer greater flexibility, scalability, and accessibility.
Benefits of Re-implementation:
ERP re-implementation offers a range of significant advantages that can transform your organization's operations and drive long-term success. Some of these benefits include:
1. Modern Architecture
Re-implementation enables the organization to take full advantage of the latest ERP architecture and features. This can include improved user interfaces, enhanced data analytics, better integration capabilities, and advanced security features.
2. Process Optimization
A fresh start provides an opportunity to redesign and optimize business processes. By analyzing and reengineering workflows, organizations can eliminate inefficiencies, streamline operations, and adopt best practices.
3. Data Cleanup
Re-implementation allows for a clean slate regarding data. Organizations can clean up old, inaccurate, or redundant data during the migration process to ensure that the new system starts with high-quality, relevant data.
For a comprehensive look at how ERP re-implementation can transform your business operations, check out our blog on '10 Ways ERP Re-implementation Can Benefit Your Business'.
Challenges of Re-implementation:
While ERP re-implementation can yield substantial benefits, it's essential to be aware of the potential challenges that may arise during the process.
1. Cost
Re-implementation is often more expensive than upgrading. The costs include new software licenses, implementation fees, and the potential downtime during the transition period. Additionally, there may be costs associated with hiring consultants and training staff on the new system.
2. Time-Consuming
The process of re-implementing an ERP system is time-consuming. It requires extensive planning, testing, and deployment. Depending on the complexity of the organization’s processes, a re-implementation project can take several months or even years to complete.
3. Training
Users need to be retrained on the new system, which can be a significant undertaking. This includes not only learning how to use the new software but also understanding any new processes or workflows that have been introduced.
Making the Decision: ERP Re-implementation vs. ERP Upgrade
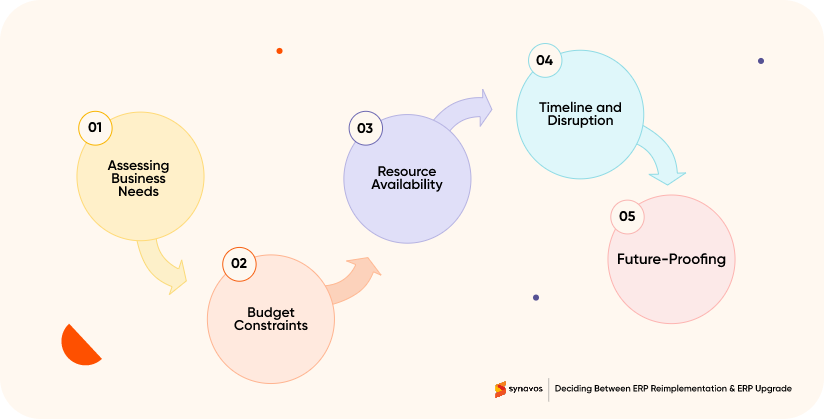
Choosing between ERP reimplementation and ERP upgrade depends on several factors, including the organization's specific needs, budget, and strategic goals. Consider these key factors when making a decision:
1. Assess Business Needs
Evaluate the current state of the ERP system and identify the primary drivers for change. Are there significant process changes or technological advancements that necessitate a complete reimplementation? Or are the desired improvements more incremental and achievable through an upgrade?
2. Budget Constraints
Consider the financial implications of both options. Reimplementation typically involves higher upfront costs, while upgrades are generally more cost-effective. Determine the available budget and weigh it against the potential benefits of each approach.
3. Resource Availability
Assess the availability of internal and external resources needed for the project. Reimplementation requires extensive planning, testing, and training, which may strain organizational resources. Upgrades, while still requiring careful planning, are generally less resource-intensive. To execute the project effectively, however, you should always work with an experienced ERP partner.
4. Timeline and Disruption
Consider the impact on business operations. Reimplementation projects are longer and more disruptive, while upgrades can be completed more quickly with minimal disruption. Evaluate the organization's ability to manage potential downtime and the impact on day-to-day operations.
5. Future-Proofing
Think about the long-term goals and future-proofing the ERP system. Reimplementation offers a fresh start with the latest technology, providing a solid foundation for future growth. Upgrades, while less transformative, can still offer significant enhancements and keep the system current.
Summing Up
ERP re-implementation and upgrading are two strategies for optimizing an ERP system. Re-implementation provides a fresh start with modern architecture and optimized processes but is costlier and more time-consuming. Upgrades are more cost-effective and less disruptive but may carry forward legacy issues. For a successful ERP transformation, both options must be carefully evaluated based on the organization's specific needs, budget, and risk tolerance.