Running a successful business today requires more than just having the best products or services; it also demands effective management of resources. That’s where Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems come into play. These systems help organizations keep track of everything from inventory to finances. But simply having an ERP system in place isn’t enough; it’s vital to integrate it with other applications, such as CRM and project management tools. This connection, known as ERP integration, is what enables smooth communication across different departments.
In this blog, we’ll discuss the concept of ERP integration, why it’s important, the benefits it offers, and the challenges you might face along the way. Let’s get started!
What is ERP Integration?
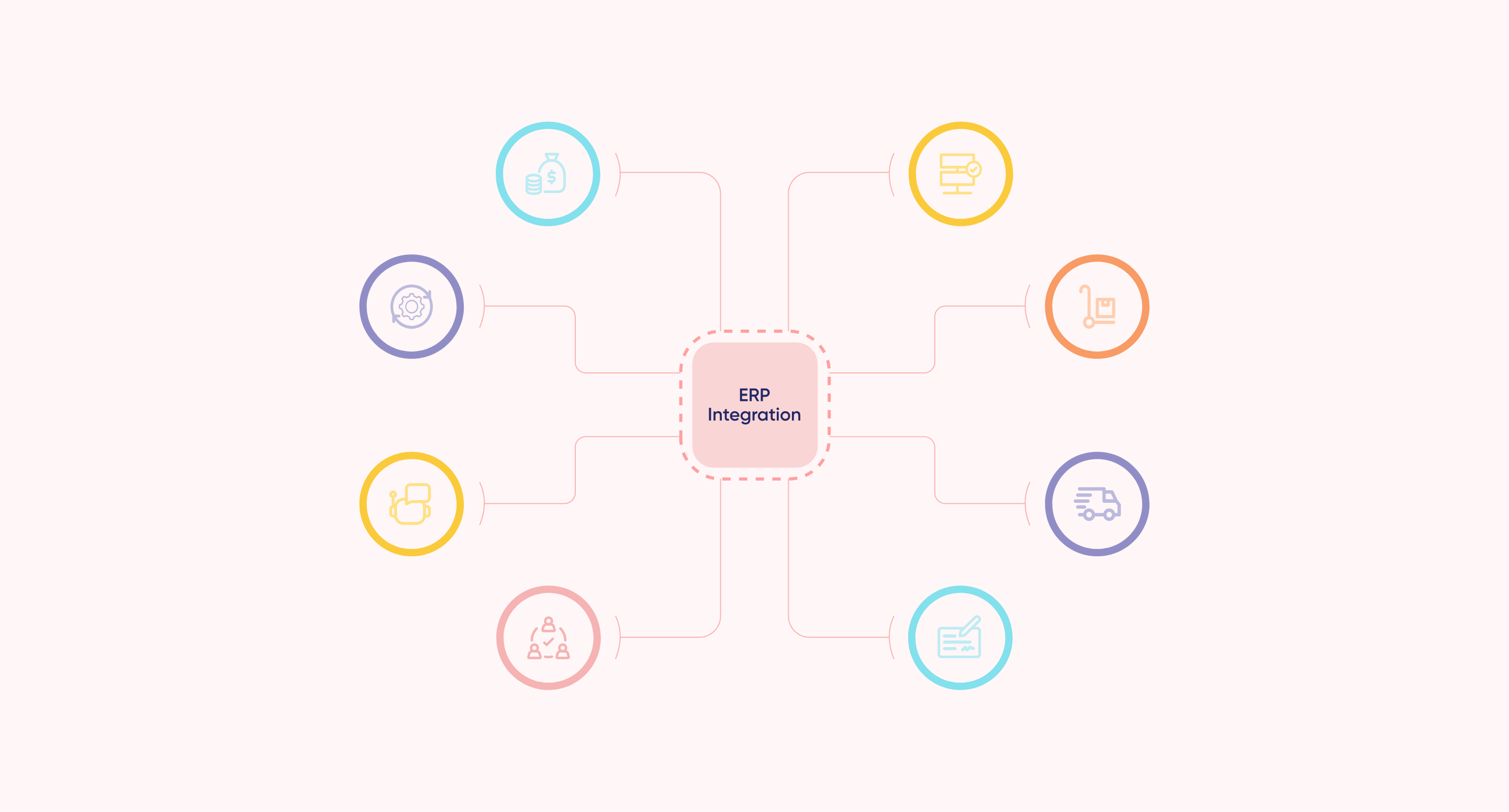
ERP integration is the process of linking an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system with other essential software applications used by a business, such as customer management tools, inventory systems, or e-commerce platforms. Without integration, each system operates separately, leading to data silos, manual updates, and potential errors. When systems are integrated, they share information automatically.
For instance, when an order is placed online, it can instantly update the inventory, finance, and customer records without any manual input. This makes operations more efficient and reduces the chances of mistakes.
Many businesses confuse ERP implementation with ERP integration, but they serve different purposes. To understand the distinction between the two, explore our blog on ERP Implementation vs. ERP Integration: What's the Difference?.
Different Methods of ERP Integration
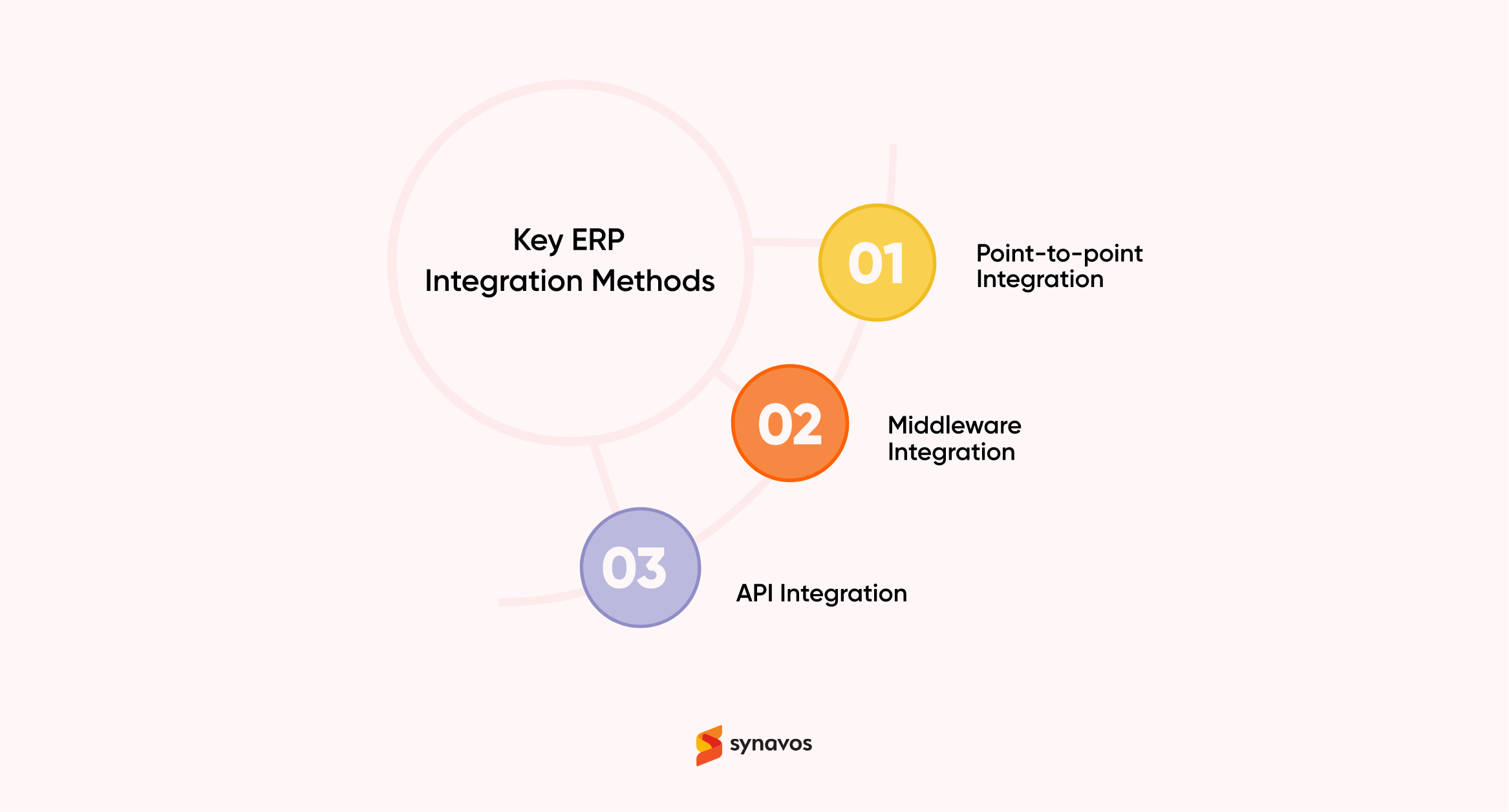
Organizations can choose from several ERP integration methods, each suited to different technological needs and approaches. Below are the three core methods of ERP integration:
1. Point-to-point Integration
Point-to-point (P2P) integration is like a straightforward handshake between two systems. In this approach, a direct connection is established between two systems, which allows them to exchange data in real time. For example, if an ERP system needs to communicate with a payroll application, a point-to-point integration would involve creating a direct link between these two platforms.
Pros:
- Easy to implement for small-scale integrations.
- Low initial costs, as only two systems are involved.
Cons:
- Scalability issues: As the number of systems increases, the complexity of managing multiple connections also rises.
- Maintenance challenges: Any changes to one system may require adjustments in all connected systems, leading to increased maintenance efforts.
2. Middleware Integration
Middleware integration involves the use of intermediary software that facilitates communication between different systems. Instead of creating direct connections, middleware serves as a bridge that enables data exchange and ensures compatibility between disparate platforms. This approach is particularly beneficial for organizations with numerous applications that need to work together.
Pros:
- Greater scalability: Middleware allows organizations to add new systems without disrupting existing integrations.
- Simplified maintenance: Changes to one system do not necessarily require adjustments in others, as the middleware handles communication.
Cons:
- Higher initial costs: Implementing middleware can be more expensive than point-to-point integration.
- Complexity: Organizations must manage and maintain the middleware itself.
3. API Integration
API (Application Programming Interface) integration involves using APIs to connect different systems, enabling them to communicate and share data. APIs are predefined sets of rules and protocols that dictate how software applications should interact. This approach has gained popularity due to its flexibility and ability to support real-time data exchange.
Pros:
- Flexibility: APIs allow organizations to integrate a wide variety of systems and applications, both on-premises and in the cloud.
- Real-time data access: APIs facilitate instant data exchange, enabling organizations to access up-to-date information.
Cons:
- Development time: Creating custom APIs can be time-consuming and may require significant technical expertise.
- Ongoing management: APIs need to be regularly updated and maintained to ensure compatibility with evolving systems.
Key Benefits of ERP Integration
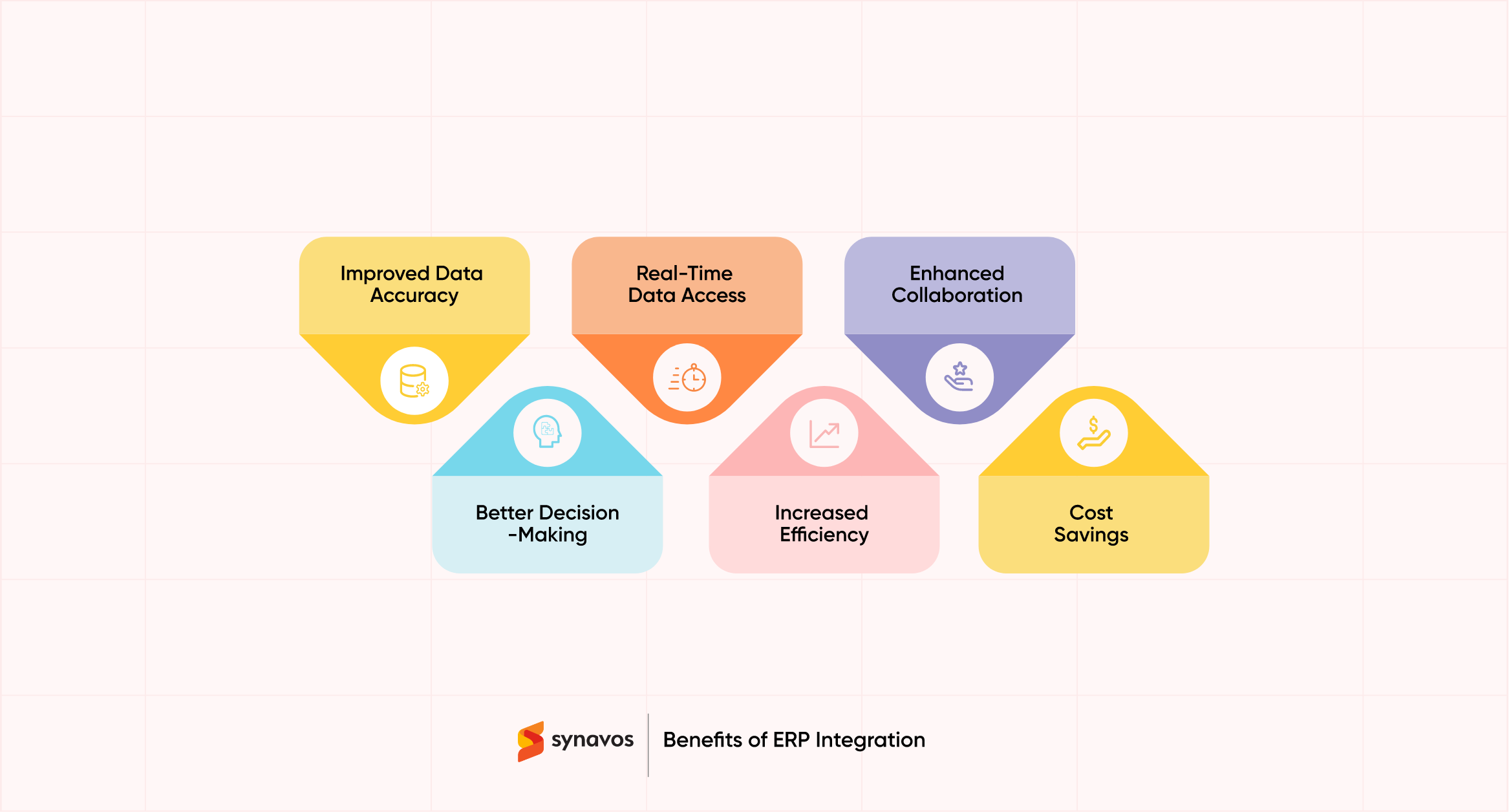
When ERP systems are integrated with other business applications, the benefits go far beyond just streamlining operations. The real impact lies in how the different facets of a business communicate seamlessly, which leads to a range of positive outcomes. Below are some of the key benefits that companies can expect from ERP integration.
-
Improved Data Accuracy
One of the primary advantages of ERP integration is that it drastically improves data accuracy. When systems work in isolation, manual data entry is often required to transfer information from one system to another. This creates room for human error—mistakes that can cause significant operational hiccups.
With ERP integration, data is automatically synchronized between systems. For example, when sales data is entered into a customer management system, it is instantly reflected in your financial records and inventory. This level of automation reduces errors and ensures that the information across your organization is consistent and up to date.
-
Real-Time Data Access
In the modern business environment, having real-time access to critical data can make all the difference. With ERP integration, employees across departments can view the most current information whenever they need it. Whether it’s a sales representative checking inventory availability, or a financial analyst reviewing up-to-the-minute cash flow reports, real-time data access means quicker response times and more informed decisions.
Instead of relying on outdated information or waiting for manual updates, your team can act immediately based on the latest data, leading to more agility and improved responsiveness to market changes.
-
Enhanced Collaboration
When data flows freely between integrated systems, it encourages better collaboration across departments. For example, sales teams can immediately see what’s happening with inventory, while the finance department has instant access to sales figures for budgeting and forecasting. This kind of visibility removes the barriers between departments, resulting in a more unified approach to business operations.
Employees no longer need to reach out to other teams to get the data they need, as they can access the same real-time information. By breaking down silos and improving transparency, ERP integration strengthens communication and teamwork, leading to a more collaborative workplace.
-
Better Decision-Making
Good decisions rely on good data, and ERP integration ensures that decision-makers have access to the right information at the right time. By connecting all your systems, you create a single source of truth where all your business data is centralized and easy to access. This enables managers and executives to analyze a complete, accurate picture of the business before making decisions.
Whether it’s deciding on a new product launch or assessing the health of your supply chain, having all relevant data in one place ensures decisions are informed, timely, and grounded in reality.
-
Increased Efficiency
Manual processes are not only time-consuming but also prone to errors. ERP integration automates many of these tasks, from transferring data between systems to generating reports, freeing up employees to focus on more value-added activities. By eliminating repetitive manual tasks, businesses can operate more efficiently, saving time and reducing the likelihood of mistakes.
For example, automated invoicing through an integrated ERP system can speed up billing cycles and improve cash flow management. In short, integration helps streamline workflows and optimizes the use of resources, making operations more efficient across the board.
-
Cost Savings
While ERP integration requires an upfront investment, the long-term cost savings can be significant. Automating manual processes, reducing data errors, and improving overall operational efficiency all contribute to reducing operational costs. With less time spent on repetitive tasks, employees can focus on strategic initiatives that drive business growth.
Moreover, with improved data accuracy and better decision-making, businesses can avoid costly mistakes and optimize their resource allocation. The reduction in wasted time and resources ultimately leads to lower operating expenses and better profit margins over time.
Common Challenges in ERP Integration
While ERP integration offers numerous benefits, the process is not without its challenges. It’s important to be aware of these obstacles so you can proactively address them. Here are some common challenges:
1. Complexity of Integration
One of the most significant challenges in ERP integration is the sheer complexity of the task, especially for businesses with multiple legacy systems or departments that use different software solutions. Integrating various platforms requires deep technical knowledge to ensure that the systems communicate effectively with one another.
Each system might have its own data structures, workflows, and limitations, making integration a complex puzzle that demands careful planning and execution. Overcoming this complexity requires not only expertise but also a clear roadmap for managing the integration process, often involving several phases to avoid disruptions to daily operations.
2. Data Migration Issues
Data migration is another common challenge when integrating ERP systems with other applications. Businesses need to transfer vast amounts of data from old systems into the new ERP solution, and this process is often fraught with difficulties. Legacy systems may store data in different formats or structures, requiring extensive cleaning and mapping before it can be successfully imported into the new system.
Without proper preparation, you risk losing valuable information or transferring inaccurate data, which could cripple operations. Ensuring data integrity and compatibility is essential, but achieving it can be a time-consuming and delicate process.
3. Customization Requirements
No two businesses are alike, which means that off-the-shelf ERP systems often don’t fully meet every company’s specific needs. Many organizations require some degree of customization to ensure the ERP system aligns with their unique processes. Customization can range from configuring workflows to creating custom modules that reflect specific industry requirements.
While customization enhances the usefulness of the system, it also complicates the integration process. Custom-built elements need to be properly integrated with other applications, and this often requires additional development work, testing, and adjustments to ensure everything functions smoothly.
4. Cost and Time Investment
The financial and time commitment required for ERP integration can be a significant hurdle, particularly for small and medium-sized businesses. ERP integration involves not only the cost of the software and any necessary hardware but also the costs associated with development, consulting, training, and ongoing maintenance.
Additionally, the integration process can take several months—or even longer, depending on the complexity of the project—during which the organization might face temporary disruptions to its operations. Many businesses underestimate these costs and timelines, which leads to budget overruns or rushed implementations that fail to deliver the desired results.
5. Security Concerns
With ERP integration, security is a paramount concern, as you’re connecting multiple systems that handle sensitive data, such as financial records, customer information, and employee details. The more systems you integrate, the more potential vulnerabilities you introduce. If not properly managed, integration can open doors for unauthorized access, data breaches, or cyberattacks.
Businesses must prioritize security measures during the integration process, including strong encryption protocols, access controls, and regular security audits. Ensuring compliance with industry regulations, such as GDPR or HIPAA, is also essential for protecting sensitive data and avoiding legal penalties.
6. Employee Resistance
Introducing a new ERP system or integrating it with existing tools often leads to changes in how employees perform their daily tasks. This can result in resistance from employees who are used to the current way of doing things or are intimidated by the learning curve associated with new systems. Resistance to change can slow down adoption and reduce the effectiveness of the integration.
To overcome this challenge, businesses need to invest in thorough employee training and provide clear communication about the benefits of the new system. Ensuring employees feel supported and involved in the transition process is key to fostering a smoother integration experience.
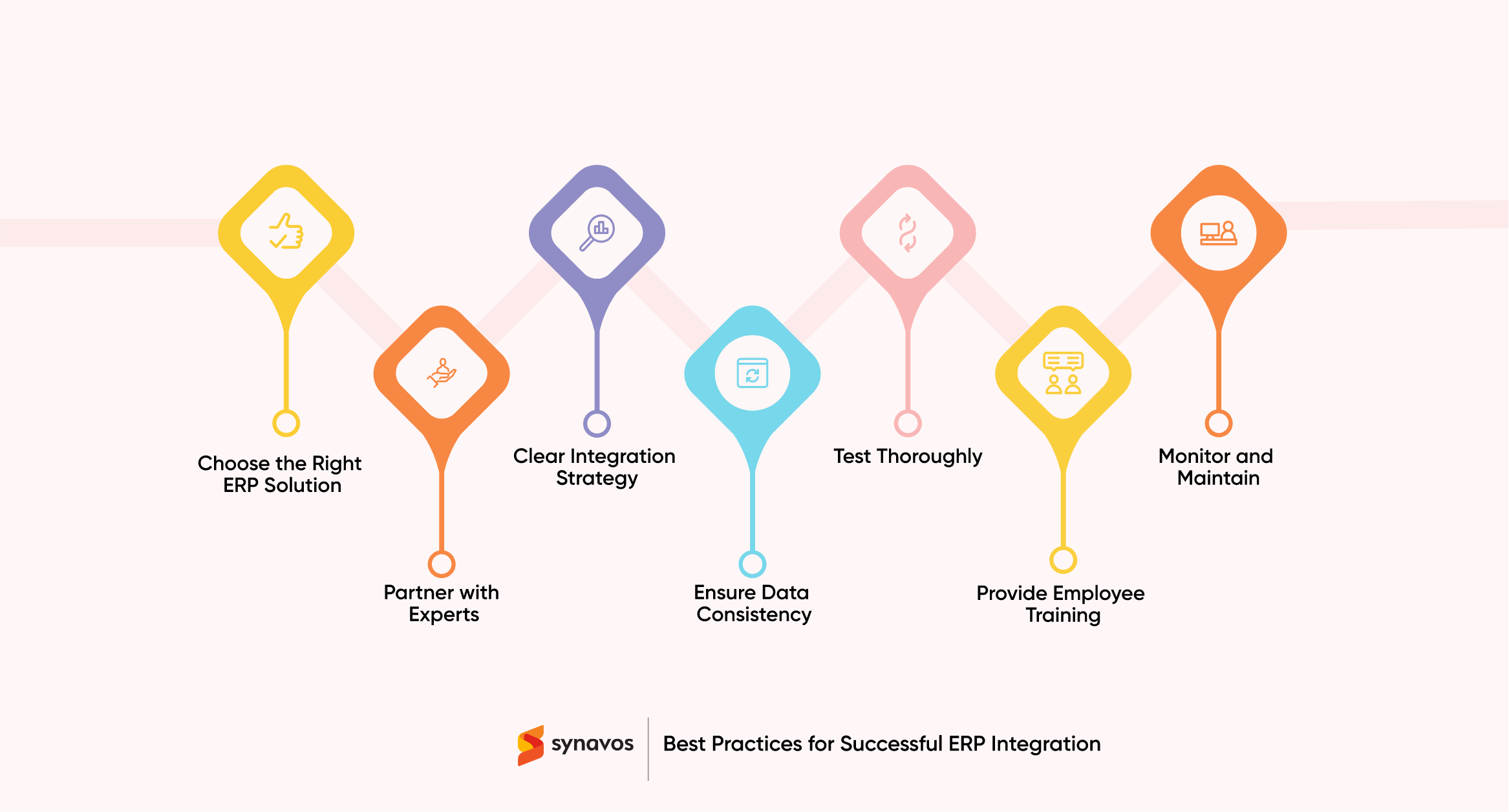
Best Practices for Successful ERP Integration
A successful ERP integration is not just about connecting systems; it’s about ensuring those systems work together smoothly to enhance business processes. To achieve this, there are several best practices that businesses should follow.
-
Choose the Right ERP Solution
The foundation of a successful ERP integration begins with selecting the right ERP solution. Not all systems are created equal, so it's important to choose one that aligns with your business's unique needs.
For example, SAP Business One is a great fit for small to midsize companies looking for robust features and scalability, while Odoo provides flexibility with its open-source framework. Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central, on the other hand, is perfect for businesses seeking a comprehensive, cloud-based solution that integrates seamlessly with other Microsoft products.
Be sure to assess your current processes and growth plans, and involve key stakeholders to ensure the ERP system you choose supports your long-term vision.
-
Partner with Experts
ERP integration is a complex task that requires specialized expertise, particularly when dealing with multiple systems or extensive customization needs. Partnering with experienced ERP consultants can significantly improve the chances of a successful implementation. These experts bring in-depth technical knowledge and practical experience, helping to identify potential challenges early on and providing tailored solutions.
Whether it’s system architecture, data migration, or security concerns, a knowledgeable partner can guide your business through each phase of the integration, ensuring that best practices are followed and the implementation stays on track.
-
Clear Integration Strategy
Having a clear and well-thought-out integration strategy is essential for avoiding confusion and delays. Before beginning the ERP integration process, outline a detailed plan that includes timelines, roles, and responsibilities, as well as any milestones or checkpoints. This plan should consider how data will flow between systems, potential challenges, and a contingency plan for any issues that might arise.
It’s also important to identify which systems and data need to be integrated first to avoid unnecessary disruptions. A step-by-step roadmap helps keep the integration on track, ensures all stakeholders are on the same page, and minimizes the risk of unexpected setbacks.
-
Ensure Data Consistency
Data consistency is key when integrating an ERP system. If the data transferred from one system to another is incomplete, inaccurate, or formatted incorrectly, it can lead to significant operational disruptions. Ensure that the data being migrated and integrated is clean, well-organized, and free from duplicates or errors. This may require conducting a data audit before the integration begins, standardizing data formats across systems, and setting up real-time data validation rules.
Ensuring that all departments are working with the same accurate and up-to-date information will prevent future inconsistencies and help the integration run more smoothly.
-
Test Thoroughly
Testing is one of the most critical steps in the ERP integration process. Before going live, conduct thorough testing of all integrated systems to ensure they work together as expected. This includes testing data flow between applications, checking for data accuracy, and ensuring that workflows function smoothly.
Involve users from different departments to participate in testing, as they will bring unique perspectives and may identify issues that were overlooked. Pilot testing or running the system in parallel with existing systems can help identify any problems without risking day-to-day operations. Testing reduces the likelihood of post-launch disruptions and gives you the opportunity to fix any issues before full deployment.
-
Provide Employee Training
No matter how well your ERP system is integrated, its success ultimately depends on how well your employees can use it. Providing comprehensive training is essential for ensuring that your staff can navigate the new system confidently and efficiently. This includes not only teaching employees how to use the system but also explaining how the integration benefits their daily tasks.
Training should be tailored to different user roles, as each department may use the system in different ways. Offering ongoing support, whether through help desks or additional workshops, will help employees adapt to the system and make the transition smoother.
-
Monitor and Maintain
ERP integration is not a one-time project but an ongoing process that requires monitoring and maintenance to ensure long-term success. After the system goes live, it’s important to continuously monitor performance to catch any issues early on, whether they involve system glitches, data discrepancies, or workflow bottlenecks.
Regular system maintenance, including updates and patches, ensures that the ERP system and its integrations remain secure and efficient. Additionally, gathering feedback from employees and making adjustments as needed can help optimize system performance over time. By committing to regular monitoring and maintenance, businesses can prevent problems from snowballing and keep their operations running smoothly.
Skyrocket Your Business Growth with Expert ERP Integration
ERP integration is more than just a tech project - it's a business transformation initiative. When done right, it can streamline your operations, improve decision-making, and give you an edge over your competitors. Yes, there are challenges along the way. But with careful planning, the right partners, and a commitment to best practices, you can overcome these hurdles and reap the substantial benefits of a well-integrated ERP system.
If you're ready to take your business to the next level with seamless ERP integration, Synavos is here to help. Our team of ERP integration experts combines deep technical knowledge with years of industry experience to deliver tailored solutions that drive real results. With everything working in harmony, your business can reach new levels of productivity and insight.

Contact us today to explore how we can help you achieve your goals!