Choosing to implement SAP isn’t just another IT decision. It’s a long-term business move that impacts everything from how your operations flow to how decisions are made. But without a clear understanding of the SAP implementation phases, even the best tools can miss the mark.
This guide breaks down each critical phase of SAP implementation, so you know what’s coming and can avoid costly mistakes.
What is SAP Implementation?
SAP implementation refers to the structured process of deploying SAP’s enterprise resource planning (ERP) software within a business. It involves a combination of strategy, system configuration, data management, and training. Each phase is critical and builds upon the last. The idea is to simplify how your business runs, covering areas like finance, HR, supply chain, and sales, all within a single, connected system.
A successful implementation isn't just about going live. It's about going live right, with clean data, trained users, and systems that support your actual business needs.
If you want your SAP project to succeed, these seven phases are where it all begins. Let’s explore them one by one.
1. Project Preparation
This is where it all begins. The project preparation phase sets the foundation for the entire implementation journey.
At this stage, your internal stakeholders and SAP implementation partner align on objectives, scope, budget, and timelines. A dedicated project team is formed, including key users, IT leads, and decision-makers. The initial roadmap is drafted, outlining milestones and responsibilities.
Key activities in this phase:
- Identifying business goals and KPIs
- Selecting the right SAP modules
- Defining roles and forming the core project team
- Choosing a reliable SAP Consulting and Implementation Firm
- Setting up basic project governance
This phase may feel like groundwork, but skipping it or rushing through often leads to issues later.
2. Business Blueprinting
Once the team is in place, the focus shifts to understanding how your business operates and how SAP can support it.
This phase involves deep-dive workshops with departments to gather requirements. Every process, from procurement and finance to inventory and HR, is mapped and reviewed. Gaps between current operations and SAP’s standard functionalities are identified. If customizations are needed, they’re defined here.
The output of this phase is the Blueprint Document, which serves as the implementation’s guiding reference.
Key highlights:
- Mapping of current (AS-IS) and future (TO-BE) processes
- Clear understanding of business needs
- Identification of necessary SAP configurations and customizations
The business blueprint phase is where vision becomes an actionable strategy.
3. Realization
Now that you know what needs to be done, it’s time to build.
The realization phase is where SAP is configured and customized based on the business blueprint. SAP consultants begin system setup, while developers work on custom elements, such as integrations, reports, forms, and more.
Configuration is done in two stages: the baseline configuration (major functions) and the final configuration (detailed refinements). Throughout, unit testing is conducted to ensure components work as expected.
What happens in this phase:
- System configuration as per blueprint
- Development of custom functionalities
- Internal testing of modules
- Ongoing reviews and feedback from stakeholders
This is also where the system begins to resemble what end-users will eventually interact with.
4. Data Migration
You can’t move to a new system without bringing your data along and doing it right matters more than many expect.
Data migration is the process of transferring data from legacy systems into SAP. But this isn't just a copy-paste job. Data often needs cleansing, formatting, and validating to align with SAP’s structure.
For businesses with years of legacy data, like Artex (the world’s largest carpet manufacturer), this step becomes even more critical. Poor data migration can undermine the whole project.
Key steps:
- Identifying what data needs to be migrated
- Cleansing and standardizing legacy data
- Mapping old data structures to SAP fields
- Validating migrated data for accuracy
Clean data ensures better reporting, decision-making, and operational performance from Day 1.
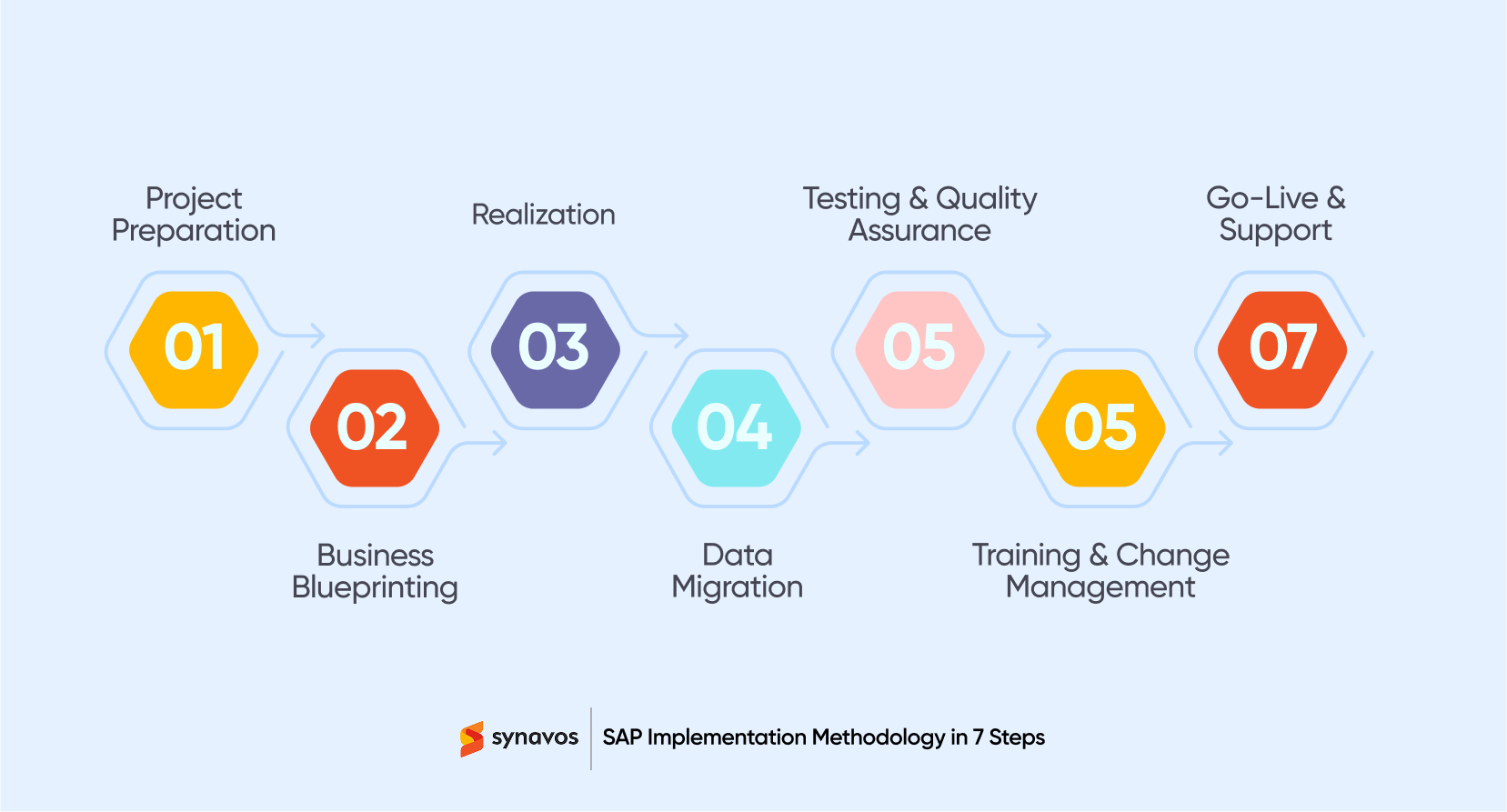
5. Testing & Quality Assurance
You wouldn’t launch a product without testing, the same goes for SAP.
This phase ensures the system works as intended, across all modules and business scenarios. Functional testing, integration testing, and user acceptance testing (UAT) are conducted to validate the setup.
End-users are involved to simulate real-life processes, ensuring nothing is missed. This phase is also used to identify performance issues and resolve last-minute bugs.
Testing tasks include:
- Scenario-based testing across departments
- Performance and load testing
- Data validation post-migration
- User acceptance testing with real users
No system is perfect at first, testing is where gaps are identified and fixed before it’s too late.
6. Training & Change Management
You’ve built the system, now you need to ensure people are ready to use it.
SAP implementation often brings significant process changes. If your teams aren’t trained properly or resist the change, adoption suffers, no matter how good the system is.
In this phase, tailored training sessions are conducted for users, focusing on their specific roles. At the same time, change management strategies are implemented to drive buy-in, reduce resistance, and communicate the benefits of the new system.
This phase includes:
- Role-based SAP user training
- Internal documentation and support material
- Change management communications
- Feedback loops to address concerns
The more confident your team feels, the smoother your go-live will be.
7. Go-Live & Post-Go-Live Support
The big day arrives but it’s not the end of the journey.
In the go-live phase, SAP becomes the primary system for all business operations. The legacy systems are shut down, and your team starts using SAP in real time.
A hypercare support period typically follows, where the project team monitors performance, addresses issues, and ensures stability. It's crucial to have experienced hands on deck to guide users and resolve unexpected problems.
What this phase includes:
- Switching from legacy to SAP
- Close monitoring of system behavior
- On-site or remote support for users
- Continuous feedback collection
A successful go-live isn’t just about turning the system on, it’s about making sure it works without disrupting your business.
Final Words
Each of the SAP implementation phases plays a vital role in the project’s success. Skip one, and you risk delays, budget overruns, or poor adoption. But when approached strategically, SAP can revolutionize how your business runs by bringing efficiency, visibility, and control like never before.
From project preparation to go-live, it’s a journey of alignment, transformation, and growth.
Ready to implement SAP with Confidence?
At Synavos, we don’t just implement SAP, we customize it to work for your business. From end-to-end implementation and large-scale data migration to user training and post-go-live support, we’ve done it all. We bring deep experience implementing SAP across industries in the Middle East and Pakistan to ensure each rollout is aligned with real business needs.
Want to see how we've helped other businesses succeed with SAP? Explore our success stories here!
Whether you're launching SAP for the first time or optimizing an existing setup, let’s talk about how SAP can actually solve your business challenges.
➤ Book a free SAP discovery session with Synavos