Is your ERP system working as hard as it should be for your business? Many companies find their ERP systems lacking in addressing their specific needs, which leads to process inefficiencies and operational challenges. ERP customization can bridge this gap by tailoring the system to align with your unique workflows and business goals. However, achieving successful ERP customization demands careful planning and precise execution.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into the world of ERP customization, covering everything from its core concepts and various types to the detailed process involved. You’ll also learn about the transformative benefits it offers and the best practices that can help you make the most out of your customization efforts. Let's start!
What is ERP Customization?
ERP customization refers to the modifications and adjustments made to an ERP system to better fit an organization’s specific processes and requirements. Unlike standard configurations that offer a set of predefined functionalities, customization involves altering the system’s core features, adding new modules, or integrating with other applications to align with your business's unique workflows.
It’s about tailoring the ERP system to work precisely how you need it to, rather than forcing your processes to adapt to the software.
Types of ERP Customization
ERP customization can take various forms, each designed to address different aspects of the system. Businesses usually leverage the following types of ERP customization:
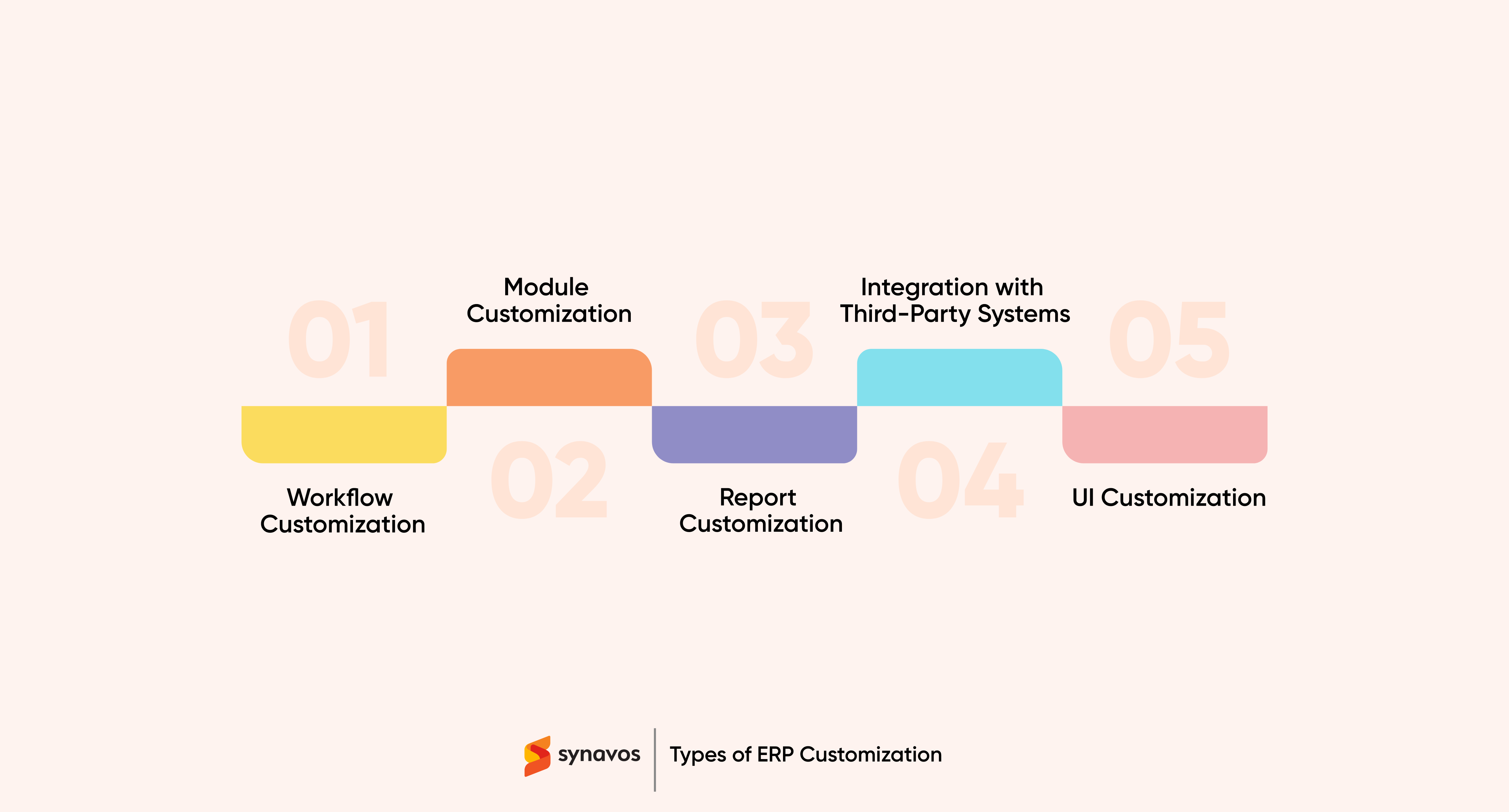
1. Workflow Customization
Workflow customization focuses on modifying the sequence of business processes and the flow of information within the ERP system. This type of customization is particularly useful for businesses with unique operational processes that are not adequately supported by standard ERP workflows. By customizing workflows, businesses can automate repetitive tasks, streamline operations, and ensure that the ERP system aligns closely with their specific ways of working.
For example, a company might customize its sales order process to include additional approval steps, notifications, or automated invoicing.
2. Module Customization
Module customization involves altering or extending the functionality of specific ERP modules to better serve particular business functions. This could mean adding new features to an existing module, integrating it with other systems, or developing entirely new modules to meet specific needs.
For example, a manufacturing company might customize its production module to incorporate industry-specific compliance requirements or integrate it with an advanced quality management system. Module customization allows businesses to enhance their ERP system’s capabilities, ensuring it delivers maximum value across different departments.
3. Report Customization
Every business relies on accurate and insightful reporting to make informed decisions. Report customization enables organizations to modify or create new reports within the ERP system to provide the information that is most relevant to them. This might involve designing custom report templates, integrating data from various sources, or setting up real-time dashboards that provide a comprehensive view of key performance indicators (KPIs).
By customizing reports, businesses can ensure they have the insights they need to drive strategic decision-making and monitor performance effectively.
4. Integration with Third-Party Systems
Most businesses use a variety of software applications to manage different aspects of their operations, from customer relationship management (CRM) systems to e-commerce platforms. Integrating these third-party systems with an ERP can significantly enhance the system’s functionality and provide a more cohesive view of business operations.
Customization in this context might involve developing custom APIs, setting up data synchronization, or creating automated workflows that bridge the gap between the ERP system and other software applications. This integration ensures data consistency, reduces manual data entry, and enables more efficient processes across the organization.
5. User Interface (UI) Customization
User interface customization focuses on modifying the ERP system’s front-end design to improve usability and user experience. This can include changing the layout of screens, adding new fields, creating shortcuts, or designing custom dashboards.
A well-customized UI can make the ERP system more intuitive and easier to use, leading to higher user adoption rates and increased productivity. Businesses can tailor the UI to meet the specific needs of different user groups, ensuring that each employee has access to the tools and information they need to perform their roles effectively.
Benefits of ERP Customization
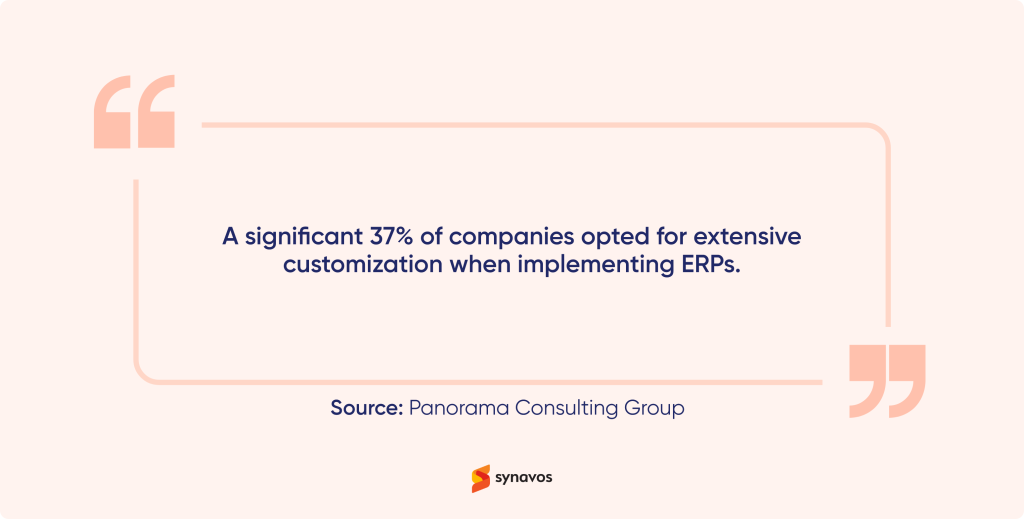
ERP customization offers a range of benefits that can significantly enhance the value of an ERP system for a business. This is why many organizations choose to invest in it—indeed, 37% opted for significant customization during their ERP implementation to fully align the system with their unique needs and achieve optimal performance.
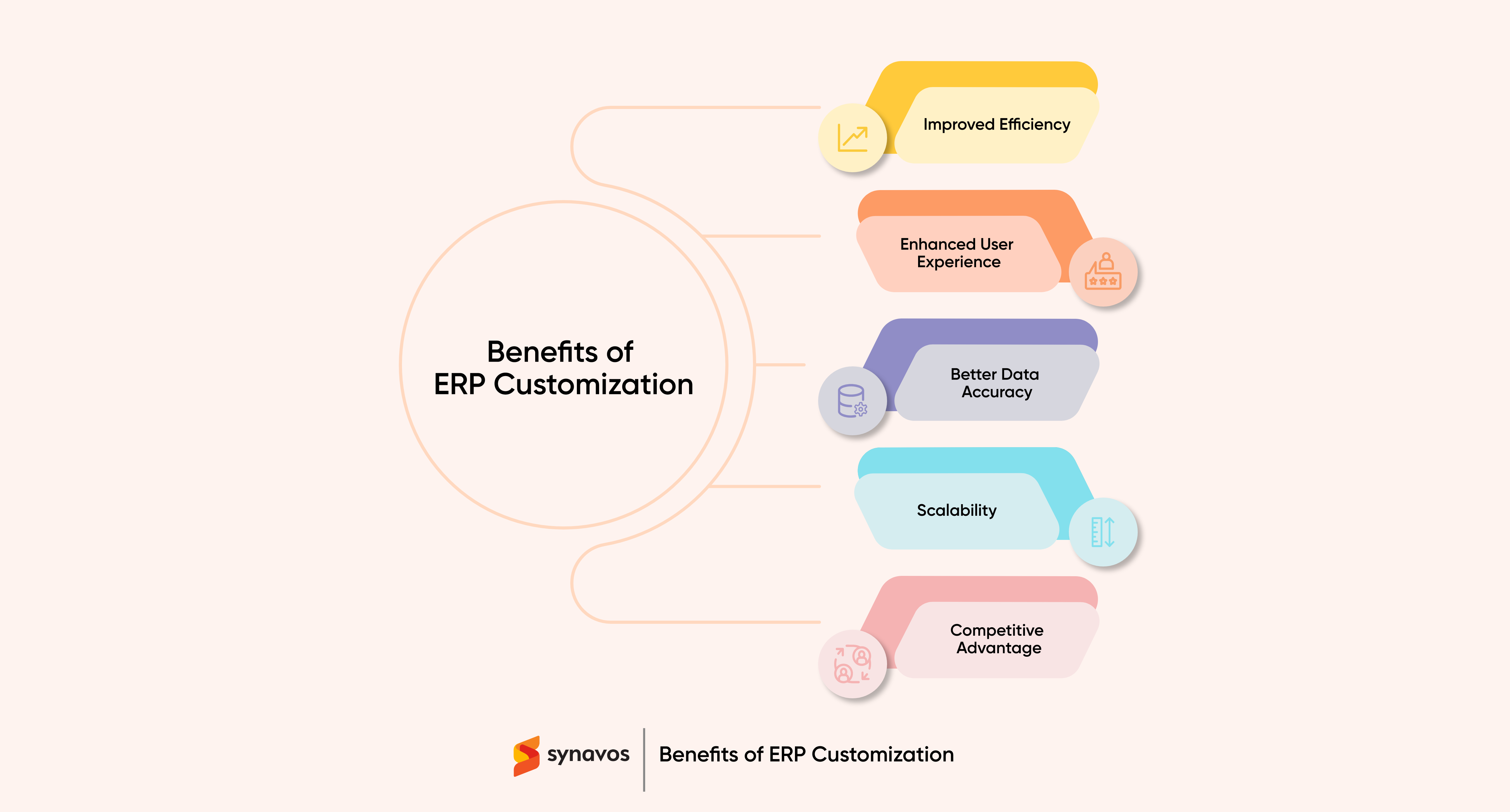
A customized ERP system provides businesses with the following advantages:
1. Improved Efficiency
One of the primary benefits of ERP customization is improved efficiency. By tailoring the ERP system to align with specific business processes, organizations can automate repetitive tasks, reduce manual data entry, and streamline operations. Customization can also eliminate bottlenecks by optimizing workflows and ensuring that the system supports the most efficient ways of working.
This leads to faster processes, fewer errors, and more productive employees, all of which contribute to overall business efficiency.
2. Enhanced User Experience
A customized ERP system can provide a much better user experience than a generic, out-of-the-box solution. Customization allows businesses to modify the user interface and functionality to better match the needs of their users, making the system more intuitive and easier to navigate.
When users find the ERP system easy to use, they are more likely to adopt it fully and utilize its features effectively. This not only improves productivity but also ensures that the organization gets the maximum value from its ERP investment.
3. Better Data Accuracy
Data accuracy is critical for effective decision-making and smooth operations. ERP customization can help improve data accuracy by automating data entry, integrating disparate systems, and setting up validation rules that reduce the likelihood of errors.
By ensuring that data is entered correctly and consistently, businesses can rely on their ERP system to provide accurate insights and reports. This, in turn, supports better decision-making and helps avoid costly mistakes caused by incorrect or incomplete information.
4. Scalability
As businesses grow and evolve, their needs change. A customized ERP system is more scalable than a standard solution because it can be adjusted and expanded to accommodate new requirements.
Whether a business is adding new users, incorporating additional modules, or integrating with other systems, a customized ERP can be adapted to meet these evolving needs. This scalability ensures that the ERP system remains a valuable asset as the business expands, providing a long-term solution that can grow with the organization.
5. Competitive Advantage
In the modern competitive world, businesses need every advantage they can get. ERP customization can provide a significant competitive edge by offering unique features and capabilities that are tailored to the specific needs of the organization.
Customization allows businesses to respond more quickly to market changes, customer demands, and regulatory requirements, thus enabling them to stay ahead of the competition. By leveraging a customized ERP system, businesses can enhance their agility, improve their responsiveness, and deliver better value to their customers.
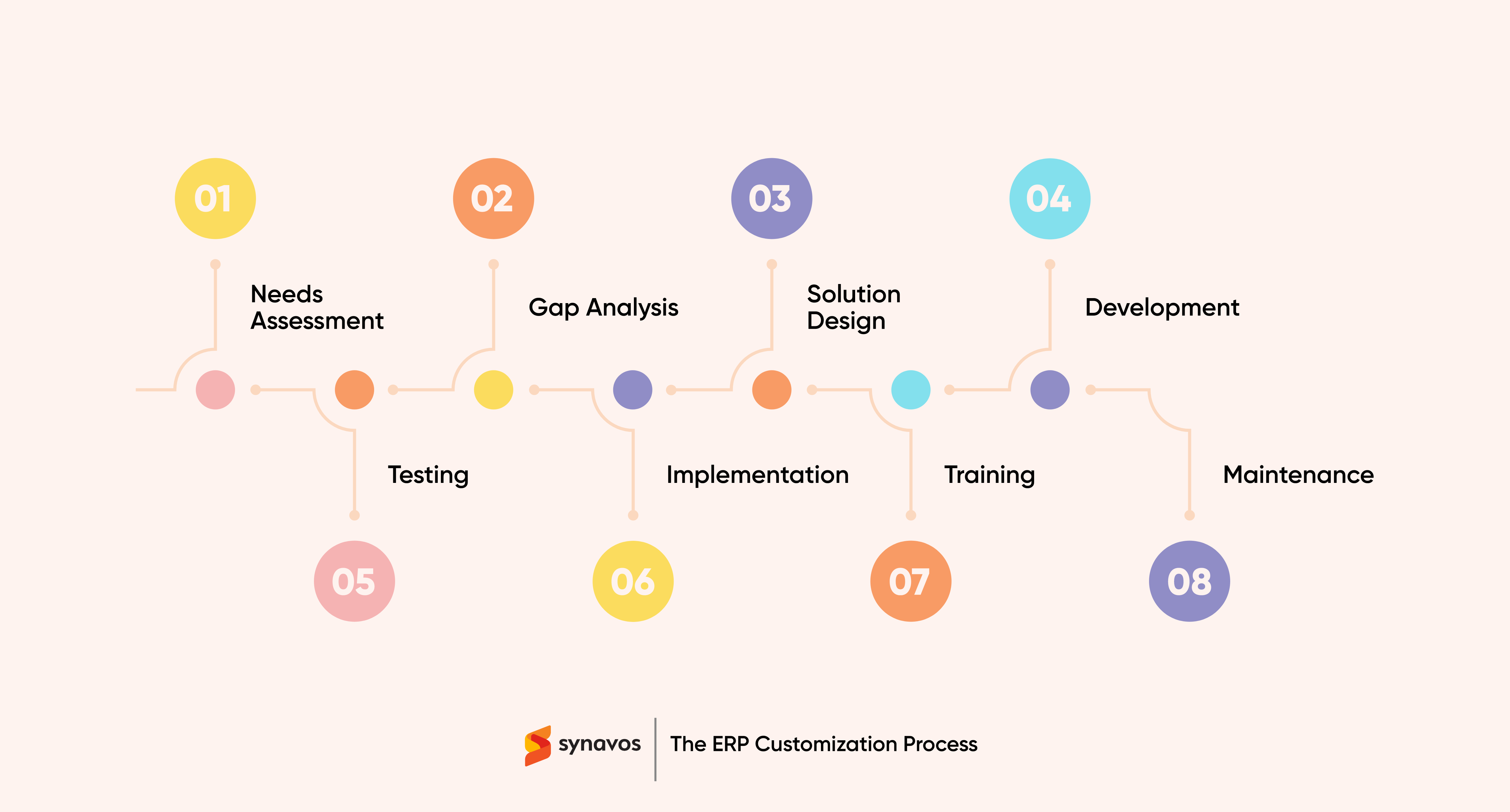
ERP Customization Process
Customizing an ERP system is a complex process that requires careful planning and execution. Here are the key steps involved in the ERP customization process:
1. Needs Assessment
The first step in the customization process is to conduct a thorough needs assessment. This involves gathering input from key stakeholders to understand their specific requirements and identify any gaps in the existing ERP system.
The needs assessment should also consider the organization’s strategic goals and objectives, ensuring that the customization aligns with the overall direction of the business. By clearly defining the needs and priorities, businesses can develop a customization plan that addresses the most critical areas and delivers the greatest value.
2. Gap Analysis
Once the needs have been identified, the next step is to perform a gap analysis. This involves comparing the current capabilities of the ERP system with the desired functionalities to identify any gaps that need to be addressed through customization.
The gap analysis helps to pinpoint specific areas where the ERP system falls short and provides a roadmap for the customization process. Additionally, it ensures that the most critical gaps are addressed first, and highlights ERP mistakes to avoid during customizations.
3. Solution Design
With a clear understanding of the needs and gaps, the next step is to design the customization solution. This involves developing a detailed plan that outlines the specific changes that need to be made, the resources required, and the timeline for implementation.
The solution design should also consider any potential risks and challenges, as well as strategies for mitigating them. By creating a comprehensive solution design, businesses can ensure that the customization process is well-planned and executed smoothly.
4. Development
Once the solution design is finalized, the development phase begins. This involves making the necessary modifications to the ERP system, which may include coding new features, altering existing functionality, or integrating third-party systems.
The development phase requires a high level of technical expertise and should be carried out by experienced developers who are familiar with the ERP system and the customization requirements. It’s important to follow best practices for software development, including version control, documentation, and code review, to ensure that the customization is of high quality and maintainable.
5. Testing
Testing is a critical step in the ERP customization process, as it ensures that the customizations work as intended and do not introduce any new issues or bugs. Testing should be conducted at multiple levels, including unit testing, integration testing, and user acceptance testing.
Unit testing focuses on individual components or features, while integration testing ensures that the customizations work seamlessly with other parts of the ERP system. User acceptance testing (UAT) is conducted with the end-users to verify that the customized ERP system meets their needs and performs as expected in a real-world environment. By thoroughly testing the customizations, businesses can identify and resolve any issues before the system goes live to minimize the risk of disruptions to operations.
6. Implementation
After successful testing, the next step is to implement the customizations in the live ERP environment. This involves deploying the changes to the production system and ensuring that everything is configured correctly. It’s essential to have a detailed implementation plan that includes a timeline, resource allocation, and a clear strategy for transitioning from the old system to the customized version.
During the implementation phase, it’s also important to monitor the system closely for any issues and be prepared to address them quickly to avoid downtime or data loss.
7. Training
Even the most well-designed and tested customizations will not deliver their full value if users are not adequately trained on how to use them. Training is a crucial part of the ERP customization process, as it ensures that all users understand the new features and functionalities and can use them effectively.
Training should be tailored to the specific needs of different user groups and should include hands-on practice, demonstrations, and support materials such as user guides and FAQs. By investing in comprehensive training, businesses can maximize user adoption and ensure that the customized ERP system is used to its full potential.
8. Maintenance
Once the customizations are implemented and users are trained, the final step is to establish a plan for ongoing maintenance. ERP systems, like all software, require regular updates and maintenance to ensure they continue to function optimally and securely. This is especially true for customized ERP systems, as custom code and features may need to be updated or modified over time to accommodate changes in the business, new regulations, or technological advancements.
A good maintenance plan should include regular reviews of the customizations, monitoring for any issues or performance problems, and a strategy for making necessary updates or improvements. By adhering to a comprehensive maintenance strategy, you can mitigate unexpected ERP customization costs and ensure your system continues to deliver value over time.
Best Practices for Successful ERP Customization
Customizing an ERP system is a significant investment, and it’s important to follow tried-and-tested tips for successful ERP customization. Here’s how to get it right:
1. Involve Key Stakeholders Early
Bringing in key stakeholders from the start is crucial. Their input will help shape the customization to fit your company’s needs and prevent any surprises later. Early involvement ensures that everyone is on the same page and supports the changes.
2. Clearly Define Requirements
Take the time to clearly outline what you need from the ERP system. Knowing exactly what features and functionalities you require helps avoid misunderstandings and keeps the project on track. Detailed requirements are essential for a smooth customization process.
3. Choose the Right Customization Partner
Finding the right partner for your ERP customization is vital. Look for someone with experience and a good reputation in your industry. The right partner will not only handle the technical side but also help you make strategic decisions to meet your business goals.

Check out the blog on "How to Choose the Right ERP Customization Partner?" for more information.
4. Opt for Scalable Solutions
Think long-term when customizing your ERP system. Choose solutions that can grow with your business and adapt to future changes. This approach helps avoid costly upgrades and keeps your system flexible as your needs evolve.
5. Conduct Rigorous Testing
Testing is a must before going live with your customized ERP. Make sure to thoroughly test all aspects of the system to catch any issues early. This includes testing for functionality, performance, and user acceptance to ensure everything works as expected.
Achieve Business Excellence with Expert ERP Customization
ERP customization is more than just a system adjustment; it's a strategic investment in your business’s future. By following the best practices we've discussed, you can ensure that your ERP system aligns perfectly with your unique processes and evolves with your business. A well-customized ERP system not only supports current needs but also positions you for future success.
At Synavos, we pride ourselves on being the leading experts in ERP customization. With a proven track record of delivering tailored ERP solutions that drive business success, our team is dedicated to crafting the perfect fit for your needs. Reach out today and let us show you how our expertise can turn your ERP system into a strategic asset!